OCS Inventory, the open-source IT asset management powerhouse, is your secret weapon for taming the wild west of your organization’s hardware and software. This isn’t your grandpappy’s spreadsheet; we’re talking about a comprehensive system that tracks everything from aging hard drives to rogue software licenses. Get ready to dive into the nitty-gritty of configuring, reporting, and optimizing your IT infrastructure with OCS Inventory.
This guide covers everything from setting up data collection and generating killer reports to integrating OCS Inventory with your existing systems and even troubleshooting those inevitable hiccups. We’ll explore its core functionalities, delve into advanced features, and even toss in a hypothetical case study to illustrate just how impactful this tool can be. Think of it as your all-access pass to mastering OCS Inventory.
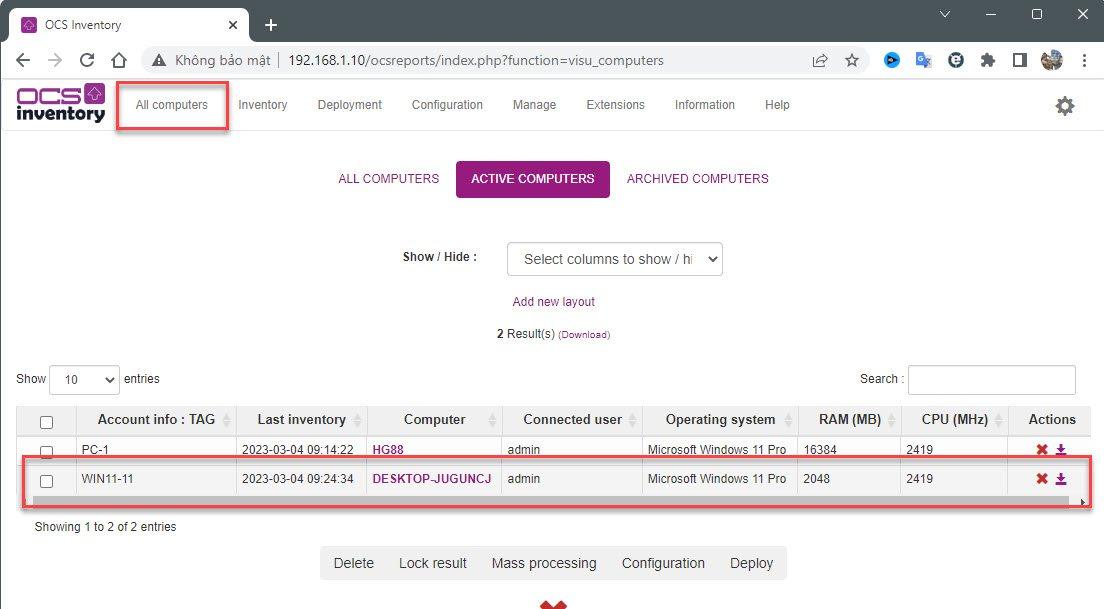
OCS Inventory Software Overview
OCS Inventory NG is a powerful, open-source software solution designed for network administrators to manage and inventory their computer hardware and software assets. It provides a comprehensive overview of your IT infrastructure, allowing for efficient troubleshooting, software deployment, and overall system management. Its flexibility and extensive feature set make it a popular choice for organizations of all sizes.OCS Inventory NG’s core functionality centers around automated hardware and software discovery and reporting.
It gathers detailed information about each machine on the network, including operating system details, installed applications, hardware components (CPU, RAM, hard drives), and network configuration. This data is then presented in a user-friendly web interface, enabling administrators to easily track assets, identify potential problems, and manage software licenses. The system also supports remote actions, allowing administrators to execute commands or deploy software updates to multiple machines simultaneously.
OCS Inventory Modules
The strength of OCS Inventory lies in its modular design. While the core functionality provides a robust inventory system, several optional modules extend its capabilities significantly. These modules cater to specific needs and can be integrated as required. For example, one module might focus on enhanced reporting and data visualization, while another might provide integration with external systems for streamlined workflow management.
The availability and specifics of these modules can vary depending on the version and specific configuration of the OCS Inventory installation. Some examples might include modules for advanced reporting, patch management, and software deployment automation.
OCS Inventory Architecture and Components
OCS Inventory NG employs a client-server architecture. Client agents are installed on each machine needing to be inventoried. These agents collect the necessary data and periodically send it to the central server. The server, typically running on a Linux machine, stores and processes the collected information, making it available through a web interface. The database (often MySQL or PostgreSQL) stores the inventory data.
The web interface provides a user-friendly dashboard for viewing reports, managing assets, and performing various administrative tasks. The interaction between the clients, the server, and the database forms the backbone of the system’s operation. A crucial component is the communication protocol used between the client agents and the server; this ensures secure and efficient data transfer. The system’s scalability depends on the server’s hardware and database configuration, allowing it to handle a large number of clients and substantial amounts of data.
Data Collection Methods in OCS Inventory

OCS Inventory NG is a powerful open-source tool for network inventory management. Its effectiveness hinges on its ability to collect comprehensive data about your hardware and software assets. This section details the methods OCS Inventory uses to gather this crucial information and provides a practical guide to configuring the system. Understanding these methods is key to optimizing your inventory management strategy.OCS Inventory employs a client-server architecture.
The client-side agent resides on each managed machine, collecting data and sending it to a central server. The server then processes and stores this information, providing a centralized view of your IT infrastructure. The data collection process is largely automated, but proper configuration is vital for accurate and comprehensive results.
OCS Inventory Configuration for Data Collection
Setting up OCS Inventory for data collection involves several steps, from installing the server and agents to configuring the communication channels and defining the data to be collected. First, you’ll need to install the OCS Inventory server on a central machine within your network. This server acts as the central repository for all collected data. Next, you’ll install the OCS Inventory agent on each client machine you wish to monitor.
This agent is responsible for collecting the hardware and software information. The server and agents communicate via a defined protocol (usually HTTPS or HTTP, with HTTPS being recommended for security). You’ll need to configure the server’s settings to specify the communication method and the location of the agents. This usually involves setting up a dedicated database (like MySQL or PostgreSQL) to store the collected inventory data.
Finally, you’ll configure the agent settings on each client machine to point to the correct server address. This allows the agents to transmit the collected data back to the central server. Regular updates to both the server and the agents are recommended to ensure optimal performance and access to the latest features and security patches.
Comparison of Data Collection Methods
OCS Inventory supports multiple data collection methods, each with its strengths and weaknesses. The primary method is agent-based, which is the most reliable and comprehensive. This method uses a dedicated client-side application installed on each machine to gather data. A secondary method, though less common and often requiring additional configurations, can utilize a combination of agent-based data and data retrieved from other sources, such as network scans or Active Directory.
The agent-based method offers better control and more detailed information, as it directly interacts with the operating system and applications. Other methods, while potentially faster for initial inventory, usually lack the depth and ongoing monitoring capabilities of the agent-based approach. The choice of method depends on your specific needs and infrastructure. For most environments, the agent-based method provides the best balance of reliability, accuracy, and comprehensiveness.
Types of Hardware and Software Information Collected
OCS Inventory collects a wide range of information about both hardware and software components. Hardware information includes details such as the computer’s manufacturer, model, processor type and speed, memory (RAM) size, hard drive capacity and type, network interface cards (NICs), and peripheral devices like printers and scanners. Software information encompasses details such as the operating system (OS) version, installed applications, service packs, patches, and drivers.
It also gathers data on user accounts, network configurations, and potentially even security software versions. The level of detail collected can be customized through configuration settings, allowing administrators to tailor the inventory to their specific needs. For instance, you might choose to collect only critical information like OS version and installed applications, or you might opt for a more granular approach, capturing details about every installed driver and service.
This flexibility allows organizations to balance the level of detail with the demands on their network and the storage capacity of their server.
Reporting and Visualization Capabilities
OCS Inventory’s strength lies not just in its data collection, but also in its ability to present that data in a clear, understandable, and actionable manner. Its reporting and visualization tools allow administrators to quickly assess the health and status of their IT infrastructure, identify potential problems, and make informed decisions about resource allocation and upgrades. This section will explore some of the key reporting and visualization features available within OCS Inventory.
OCS Inventory offers a robust suite of reporting and visualization tools, enabling IT administrators to gain valuable insights into their hardware and software assets. These tools provide various methods for analyzing collected data, from simple summaries to complex visualizations. The flexibility of the system allows for customization of reports to meet specific needs, enhancing the efficiency of IT management.
Sample Hardware Asset Report, Ocs inventory
This report summarizes key hardware assets within the organization. Imagine a report detailing the number of computers, their operating systems, processors, and RAM. It could further segment this data by department, allowing IT to quickly see which departments have the oldest or most resource-intensive machines. For instance, the “Sales” department might show a higher proportion of older machines compared to the “Engineering” department, indicating a potential need for upgrades or replacements.
This report would be presented in a tabular format, possibly including filtering and sorting options for easier navigation. The data would be easily exportable to a spreadsheet for further analysis.
Software License Usage Visualization
A visual representation of software license usage can be created using a variety of charts and graphs. A simple bar chart could display the number of licenses used for each software package. A more sophisticated visualization might use a stacked bar chart to show the breakdown of license usage across different departments or user groups. For example, a stacked bar chart could illustrate that while the “Marketing” department has the most licenses for Adobe Creative Suite, a significant portion of those licenses remain unused, highlighting potential for optimization.
This visual representation allows for quick identification of over- or under-utilized software licenses.
Software Distribution Across Departments
| Department | Software | License Count | Usage Rate |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sales | Microsoft Office | 25 | 95% |
| Engineering | AutoCAD | 15 | 100% |
| Marketing | Adobe Creative Suite | 30 | 60% |
| IT | SolarWinds | 5 | 100% |
Integrating OCS Inventory with Other Systems
OCS Inventory’s power significantly increases when integrated with other systems within your IT infrastructure. Seamless data exchange streamlines workflows, improves efficiency, and provides a more holistic view of your IT assets. Effective integration allows for automated processes and reduces manual data entry, saving time and minimizing errors. This section explores several key integration methods.OCS Inventory offers various avenues for integration, primarily leveraging its robust export capabilities and API (though the API might require more technical expertise).
These methods enable a dynamic link between OCS Inventory and other critical systems, enriching your IT management capabilities.
Integrating OCS Inventory with a Ticketing System
Connecting OCS Inventory to a ticketing system, such as Jira, ServiceNow, or Zendesk, automates incident resolution and asset tracking. When a ticket is created reporting a hardware or software issue, the ticketing system can query OCS Inventory for detailed information about the affected asset. This instantly provides technicians with crucial details like the asset’s specifications, operating system, and installed software, speeding up troubleshooting and repair.
For example, if a user reports a slow computer, the integrated system could automatically pull up the computer’s specifications from OCS Inventory, revealing insufficient RAM as the likely culprit. This automation reduces the time spent gathering information and allows technicians to focus on resolving the issue. The integration typically involves configuring the ticketing system to access OCS Inventory’s data via its export functions or, for more advanced scenarios, using its API.
Integrating OCS Inventory with a CMDB (Configuration Management Database)
Integrating OCS Inventory with a CMDB, such as BMC Remedy, ServiceNow CMDB, or an internally developed CMDB, creates a central repository of IT asset information. This integration ensures data consistency and eliminates data silos. OCS Inventory can automatically populate the CMDB with discovered hardware and software details, maintaining an accurate and up-to-date inventory. For instance, when new hardware is added to the network, OCS Inventory automatically detects it and pushes the relevant data (manufacturer, model, serial number, etc.) to the CMDB, avoiding manual updates.
This automation enhances the CMDB’s accuracy and reliability, providing a single source of truth for all IT assets. The method of integration typically involves using OCS Inventory’s export functionalities to feed data into the CMDB’s import mechanisms or through direct API interaction.
Exporting OCS Inventory Data to a Spreadsheet or Database
OCS Inventory provides straightforward methods for exporting collected data. This allows for easy analysis and reporting using familiar tools. Data can be exported in various formats, including CSV, XML, and SQL. This flexibility enables integration with spreadsheet software like Microsoft Excel or Google Sheets, and database management systems like MySQL or PostgreSQL. For example, exporting data to a spreadsheet allows for simple filtering and sorting to identify specific assets or trends.
Exporting to a database allows for more complex queries and analysis using SQL. This export functionality is crucial for creating custom reports or integrating the data with other analytical tools. The process typically involves selecting the desired export format within the OCS Inventory interface and specifying the data fields to include.
Security Considerations for OCS Inventory
OCS Inventory, while a powerful tool for managing IT assets, introduces several security risks if not properly configured and maintained. A robust security posture is crucial to protect sensitive data and prevent unauthorized access to your network infrastructure. This section details potential vulnerabilities and Artikels mitigation strategies to ensure the security of your OCS Inventory deployment.Securing OCS Inventory involves a multi-layered approach encompassing server-side, client-side, and access control measures.
Failure to address these aspects can lead to data breaches, system compromises, and disruptions to your IT operations. Effective security practices are paramount for maintaining the integrity and confidentiality of your inventory data.
Server-Side Security
Securing the OCS Inventory server is paramount. This involves implementing strong passwords for all administrative accounts, regularly updating the server’s operating system and OCS Inventory software to patch known vulnerabilities, and enabling robust firewall rules to restrict access to only necessary ports. Implementing a strong intrusion detection system (IDS) or intrusion prevention system (IPS) can also provide an additional layer of defense against malicious activity.
Regular security audits and penetration testing are recommended to identify and address potential weaknesses proactively. Consider utilizing a dedicated, isolated server for OCS Inventory, minimizing the attack surface.
Client-Side Security
Client-side security focuses on protecting the agents deployed on managed devices. This begins with deploying only signed agents to prevent unauthorized modifications or malicious code injection. Regularly updating the client agents is crucial to benefit from the latest security patches. Restricting agent communication to only the designated OCS Inventory server through firewall rules helps prevent unauthorized access or data exfiltration.
Furthermore, implementing strong encryption for all communication between the clients and the server protects the data transmitted during inventory scans. Consider using HTTPS for all communications.
User Access and Permissions
Effective management of user access and permissions is vital to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive inventory data. Implement the principle of least privilege, granting users only the necessary permissions to perform their tasks. Regularly review and update user permissions to reflect changes in roles and responsibilities. Employ strong password policies, enforcing password complexity, regular changes, and account lockout policies to mitigate brute-force attacks.
Multi-factor authentication (MFA) adds an extra layer of security, making it significantly harder for unauthorized individuals to access the system. Detailed audit logs should be maintained to track user activity and identify potential security breaches. Regularly review these logs for suspicious activity.
Managing Software Licenses with OCS Inventory
OCS Inventory offers a powerful, albeit often overlooked, capability for managing software licenses across your network. By leveraging its robust data collection and reporting features, you can gain valuable insights into your software landscape, ensuring compliance and avoiding costly licensing violations. Effective license management using OCS Inventory contributes to better budget control, reduced risk, and improved overall IT efficiency.OCS Inventory doesn’t directly manage licenses; it provides the data necessary for effective license management.
This means integrating OCS Inventory with your existing license management system or using its reporting features to create a custom tracking system is crucial. The process involves collecting software inventory data, analyzing that data to identify potential compliance issues, and then generating reports to visualize the findings.
Tracking Software Licenses Using OCS Inventory
A procedure for tracking software licenses using OCS Inventory involves several key steps. First, ensure OCS Inventory is configured to collect detailed software information, including the software name, version, and ideally, license keys (if stored locally). Next, regularly schedule inventory scans to maintain an up-to-date record of software installed on each machine. This data can then be exported or queried directly within OCS Inventory’s interface to create a comprehensive software inventory.
Finally, compare this inventory against your purchased license records to identify any discrepancies. This comparison can be done manually, using spreadsheets, or by integrating OCS Inventory with a dedicated license management system through scripting or APIs. Regular updates of both your software inventory and your license database are critical to maintaining accuracy.
Identifying Unlicensed Software Using OCS Inventory Data
Identifying unlicensed software involves analyzing the OCS Inventory data to pinpoint software installations that lack corresponding licenses. This process typically begins by generating a report showing all installed software, along with the number of installations. This report is then compared to a list of licensed software, identifying any software present on the network that isn’t accounted for in your license inventory.
For example, if your license records indicate you have 10 licenses for Adobe Photoshop, but OCS Inventory reports 15 installations, you know you have 5 unlicensed instances. Automated scripts can be developed to streamline this comparison process and automatically flag potential compliance issues. The key here is having accurate and up-to-date license information.
Generating Reports on Software License Compliance
OCS Inventory provides several methods for generating reports on software license compliance. The simplest method involves using the built-in reporting features to create custom reports based on software names, versions, and the number of installations. These reports can be filtered to highlight software with a high number of installations exceeding the purchased license count. More sophisticated reporting can be achieved by exporting the data to a spreadsheet program (like Excel or LibreOffice Calc) or a database for advanced analysis and visualization.
Custom reports can be designed to show compliance percentages for specific software packages or across the entire organization, providing a clear overview of your licensing situation. For instance, a report might display a list of all software packages, their license counts, the number of installations, and a calculated compliance percentage for each. This allows for easy identification of areas needing immediate attention.
Troubleshooting Common OCS Inventory Issues

OCS Inventory, while generally robust, can sometimes present challenges. This section Artikels common problems and their solutions, helping you keep your inventory management running smoothly. Addressing these issues promptly minimizes downtime and ensures accurate data collection.
OCS Inventory Installation Problems
Successful installation hinges on several factors. Common problems include insufficient permissions, conflicts with existing software, or incorrect configuration settings. Addressing these often requires careful review of the installation logs and system requirements.
- Permission Errors: The OCS Inventory server and client components require specific permissions to function correctly. Insufficient privileges can manifest as installation failures or inability to access necessary system resources. Solutions involve verifying that the user account performing the installation has the necessary administrator or root privileges, and checking file permissions for directories where OCS Inventory is installed.
- Software Conflicts: Conflicts with other software, particularly other inventory management tools or network services, can interfere with installation. This often results in unexpected errors or failures during the installation process. Careful examination of running processes and services before installation, and potentially uninstalling conflicting applications, can resolve these issues. Checking the OCS Inventory documentation for compatibility information with other software is also vital.
- Incorrect Configuration: Incorrectly configured settings in the OCS Inventory server configuration files can prevent the server from starting or functioning correctly. This can lead to installation failures or unexpected behavior after installation. Carefully review the server configuration files, paying attention to database connections, network settings, and other critical parameters. Consult the OCS Inventory documentation for correct configuration examples and best practices.
Troubleshooting Client-Server Connectivity Issues
Connectivity problems between OCS Inventory clients and the server are a frequent source of data collection failures. These issues usually stem from network misconfigurations, firewall restrictions, or problems with the OCS Inventory agent on the client machines.
- Network Configuration: Ensure that clients can reach the OCS Inventory server using the correct IP address or hostname. Check network connectivity using tools like
pingortracerouteto identify network bottlenecks or connectivity problems. Verify that the network is correctly configured, including DNS resolution and network address translation (NAT) settings, if applicable. - Firewall Restrictions: Firewalls on both the client and server machines might block the necessary communication ports used by OCS Inventory. Temporarily disabling the firewall (for testing purposes only) can help determine if this is the issue. If so, configure the firewall to allow communication on the relevant ports, typically TCP ports 80 and 443. Refer to the OCS Inventory documentation for the exact port numbers required.
- Agent Problems: Problems with the OCS Inventory agent on the client machines can prevent them from communicating with the server. Check the agent’s logs for errors or warnings. Restarting the agent or reinstalling it might resolve the issue. Ensure the agent is properly configured and running on the client machines. Consider using a remote management tool to troubleshoot agent-related problems on clients.
Resolving Data Synchronization Errors
Data synchronization errors occur when data fails to transfer correctly between clients and the server. This can lead to incomplete or inaccurate inventory data.
- Database Issues: Problems with the OCS Inventory database, such as insufficient disk space, database corruption, or incorrect database configuration, can cause synchronization failures. Regular database backups are crucial. Check disk space, repair the database if necessary, and verify database settings.
- Network Connectivity (Revisited): As mentioned before, poor network connectivity can interrupt data synchronization. Re-examine network connectivity issues between clients and the server, paying particular attention to network latency and bandwidth.
- Agent Configuration Errors: Incorrectly configured OCS Inventory agents on client machines might fail to properly transmit data. Review agent settings and ensure they are correctly pointing to the server. Check the agent logs for errors or warnings related to data transmission.
Advanced Features and Customization

OCS Inventory’s power extends far beyond basic hardware and software discovery. Its advanced features and customization options allow for significant tailoring to meet specific organizational needs, boosting efficiency and providing deeper insights into your IT infrastructure. This section explores these capabilities, focusing on scripting, report customization, and plugin integration.
OCS Inventory offers a robust framework for extending its core functionality. This flexibility allows administrators to automate repetitive tasks, create custom reports tailored to their specific requirements, and integrate OCS Inventory seamlessly with other systems in their IT environment.
Scripting and Automation
OCS Inventory supports scripting, primarily through its agent-side capabilities. This allows administrators to automate various tasks, such as collecting specific data not natively supported, performing custom actions on discovered assets, or triggering automated responses based on inventory data. For example, a script could automatically uninstall outdated software identified by OCS Inventory, or generate a custom report detailing only critical security vulnerabilities.
These scripts are typically written in languages like Bash (for Linux/macOS agents) or PowerShell (for Windows agents), allowing for extensive control over data collection and post-processing. The specific scripting capabilities and supported languages may vary depending on the OCS Inventory version and agent operating system.
Customizing Reports and Dashboards
The default reports provided by OCS Inventory are comprehensive, but they might not perfectly align with every organization’s unique needs. Fortunately, OCS Inventory allows for substantial customization of reports and dashboards. This involves modifying existing reports to include or exclude specific data points, creating entirely new reports from scratch, and altering the visual presentation of data through custom templates.
While the exact methods for report customization may vary slightly between OCS Inventory versions, generally it involves working with the reporting engine’s configuration files and possibly employing custom SQL queries to extract and format the desired data. This allows for creating reports focused on specific metrics, such as software license compliance, hardware utilization, or security vulnerability trends, presented in a manner most useful to the organization.
Extending Functionality with Plugins and Custom Scripts
OCS Inventory’s architecture allows for extending its capabilities through plugins and custom scripts. Plugins offer a structured approach to adding new features, often involving integrating with external systems or adding new data collection methods. Custom scripts, on the other hand, provide a more flexible approach for addressing specific, unique needs.
So, we’re tracking software licenses with OCS Inventory, right? It’s pretty crucial to know what’s on each machine, especially considering security. Making sure every Windows 10 machine has a solid antivirus program is key, and that’s where checking out resources like antivirus for windows 10 comes in handy. Then, we can use OCS Inventory to verify that the chosen antivirus is actually installed and updated across the board.
The process of implementing plugins typically involves downloading the plugin, installing it according to the provided instructions, and configuring it to interact with OCS Inventory. Custom scripts, as previously mentioned, are written to perform specific tasks, often triggered by events within OCS Inventory or scheduled to run periodically. For instance, a custom script could automate the process of generating compliance reports, or integrate OCS Inventory data with a ticketing system for automated incident management.
Deployment and Maintenance Strategies
Successfully deploying and maintaining OCS Inventory in a large organization requires a well-defined plan encompassing initial setup, ongoing updates, and robust data protection. This involves careful consideration of network infrastructure, user permissions, and a proactive approach to potential issues. Failing to plan for these aspects can lead to significant downtime and data loss.Deploying OCS Inventory across a large organization necessitates a phased approach to minimize disruption and ensure a smooth transition.
A comprehensive rollout strategy considers the organization’s size, network topology, and existing IT infrastructure. Proper planning also minimizes potential conflicts with other systems and reduces the risk of deployment errors.
Deployment Plan for a Large Organization
A phased rollout is crucial for minimizing disruption. The initial phase might focus on a pilot group of computers in a less critical department, allowing for testing and refinement of the deployment process before wider implementation. Subsequent phases can involve expanding deployment to other departments, gradually increasing the number of managed devices. Thorough testing at each stage is essential to identify and resolve any potential problems before they affect a large number of users.
Detailed documentation of each phase, including configurations and troubleshooting steps, is also highly recommended. Consider using a ticketing system to track issues and progress during the rollout.
Maintenance Schedule for Regular Updates and Patching
Regular updates and patching are critical for maintaining the security and stability of OCS Inventory. A scheduled maintenance window, perhaps during off-peak hours or weekends, should be established to minimize disruption to users. The frequency of updates will depend on the release cycle of OCS Inventory and the severity of any security vulnerabilities identified. An automated update system can streamline the process, ensuring that all components are kept up-to-date.
It’s essential to thoroughly test updates in a non-production environment before deploying them to the entire system. A change management process, documenting all updates and their impact, is vital for maintaining system integrity and traceability.
Backing Up and Restoring OCS Inventory Data
Regular backups are essential for protecting valuable inventory data. A robust backup strategy should include both full and incremental backups, stored in a secure and geographically separate location. The frequency of backups should be determined by the rate of data change and the organization’s recovery point objective (RPO) and recovery time objective (RTO). For example, a financial institution might require daily full backups, while a smaller organization might find weekly backups sufficient.
Testing the restoration process regularly is critical to ensure that the backups are valid and that the restoration process works as expected. Consider using a version control system for configuration files to facilitate easy rollback in case of errors. This helps maintain a complete history of system configurations and allows for quick recovery from unintended changes.
Cost Optimization Using OCS Inventory Data
OCS Inventory’s comprehensive data collection capabilities offer a powerful tool for optimizing IT spending. By providing a detailed snapshot of your hardware and software assets, OCS Inventory allows for informed decisions leading to significant cost savings across your IT infrastructure. This involves strategically managing hardware, consolidating software licenses, and identifying underutilized resources.
Leveraging the data collected by OCS Inventory, organizations can proactively address areas of potential cost overrun, leading to more efficient resource allocation and a healthier IT budget. This section will Artikel practical strategies for achieving these cost optimizations.
Hardware Cost Optimization Strategies
Effective hardware cost optimization relies on understanding your current asset inventory and identifying areas for improvement. OCS Inventory provides the necessary data to make informed decisions about hardware upgrades, replacements, and disposals. By analyzing data on hardware age, utilization rates, and performance metrics, organizations can identify potential cost savings. For example, identifying older machines nearing end-of-life allows for proactive planning of replacements, avoiding costly emergency repairs or unexpected downtime.
Similarly, pinpointing underutilized servers can lead to consolidation efforts, reducing energy consumption and maintenance costs. OCS Inventory reports can show the age and model of each machine, along with its CPU utilization, memory usage, and disk space. This data enables a more strategic approach to hardware lifecycle management.
Software License Consolidation Opportunities
OCS Inventory’s ability to scan and identify installed software across your network is invaluable for software license management. By analyzing the software inventory data, you can pinpoint instances of over-licensing, identify unused software licenses, and potentially negotiate better deals with vendors. For instance, OCS Inventory might reveal that 50 licenses of a particular software were purchased, but only 30 are actively being used.
This information allows for a reduction in the number of licenses purchased in the future, saving significant costs. Furthermore, the detailed software inventory can facilitate the identification of software that has been superseded by newer versions, allowing for more efficient licensing and streamlined software deployments.
Identifying Underutilized or Redundant Hardware Assets
OCS Inventory’s reporting features can be used to identify underutilized or redundant hardware assets. This includes servers with low CPU utilization, workstations with minimal usage, or network devices with limited activity. By analyzing historical data on hardware usage, organizations can identify patterns of underutilization and make informed decisions about consolidating or decommissioning these assets. For example, a server consistently operating below 20% capacity might be a candidate for consolidation with other servers, reducing energy costs and maintenance overhead.
Similarly, workstations that haven’t been accessed for extended periods might be repurposed or removed from the network entirely, freeing up valuable resources and reducing the overall IT footprint. This data-driven approach to asset management helps prevent unnecessary hardware expenses and improve overall IT efficiency.
Case Study: Successful Implementation of OCS Inventory at Acme Corporation
Acme Corporation, a mid-sized manufacturing company with over 500 employees and a diverse IT infrastructure, faced significant challenges in managing its hardware and software assets. Manual inventory processes were time-consuming, error-prone, and lacked the detail needed for effective IT planning and budgeting. The company decided to implement OCS Inventory to streamline its asset management and improve overall IT efficiency.
Implementation Process and Challenges
The implementation of OCS Inventory at Acme Corporation was a phased approach. First, a pilot program was conducted in a smaller department to test the software’s functionality and identify potential issues. This allowed the IT team to refine their deployment strategy and address any unforeseen problems before rolling out the software company-wide. One significant challenge was integrating OCS Inventory with the company’s existing Active Directory system.
This required careful configuration and testing to ensure seamless data synchronization. Another challenge was the need to train employees on how to use the new system. Acme addressed this through a combination of online training modules and hands-on workshops.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)
Several KPIs were used to measure the success of the OCS Inventory implementation. These included:
- Reduction in time spent on manual inventory tasks: Before OCS Inventory, manual inventory took approximately 20 hours per month. After implementation, this was reduced to less than 5 hours per month, a 75% reduction.
- Accuracy of asset data: The accuracy of asset data increased from approximately 80% to over 98% following implementation.
- Improved software license compliance: OCS Inventory provided a clear overview of software licenses, helping Acme avoid potential legal and financial penalties. The number of software license compliance issues was reduced by 60%.
- Reduced IT support costs: By providing detailed information about hardware and software, OCS Inventory helped the IT team resolve support issues more efficiently, reducing resolution time and overall support costs by 20%.
Impact on IT Operations and Efficiency
The implementation of OCS Inventory significantly improved IT operations and efficiency at Acme Corporation. The automated data collection eliminated the need for manual inventory, freeing up IT staff to focus on more strategic tasks. The detailed reporting and visualization capabilities provided by OCS Inventory enabled better capacity planning and informed decision-making regarding hardware and software purchases. The software also facilitated proactive maintenance and reduced downtime by providing early warnings of potential hardware failures.
Finally, the improved software license management helped Acme optimize its software spending and avoid unnecessary expenses.
End of Discussion
So, there you have it – a comprehensive look at OCS Inventory NG. From initial setup and data collection to advanced features and optimization strategies, we’ve covered a lot of ground. Remember, mastering OCS Inventory isn’t just about knowing the software; it’s about leveraging its power to streamline your IT operations, optimize costs, and ultimately, keep your tech running smoothly.
Now go forth and conquer your IT asset management challenges!
Query Resolution
What’s the difference between OCS Inventory NG and the older versions?
OCS Inventory NG is a complete rewrite, offering improved performance, security, and features compared to older versions. It’s the current, actively maintained and supported version.
Can OCS Inventory handle large networks with thousands of devices?
Yes, OCS Inventory is designed to scale. Performance may vary depending on network infrastructure and server resources, but it can handle significant numbers of devices with proper configuration.
Is OCS Inventory compatible with all operating systems?
OCS Inventory supports a wide range of operating systems, including Windows, macOS, and various Linux distributions. Check the official documentation for the most up-to-date compatibility list.
How much does OCS Inventory cost?
OCS Inventory NG is open-source and completely free to use. There are no licensing fees.
Where can I find more detailed documentation and support?
The official OCS Inventory NG website and community forums are excellent resources for documentation, tutorials, and troubleshooting assistance.


